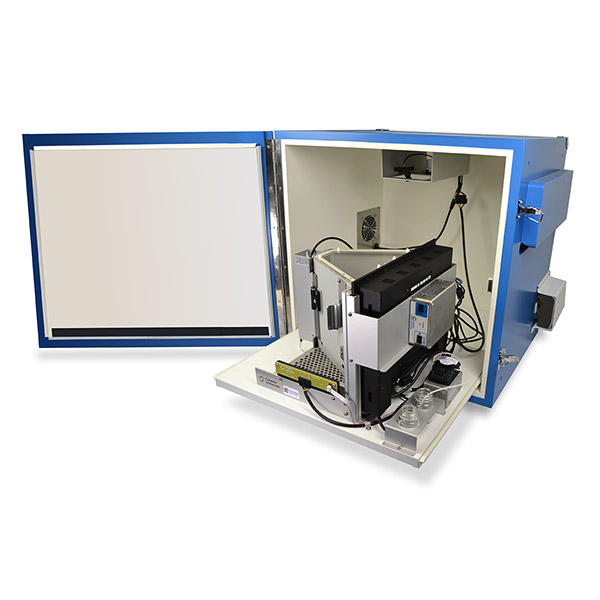
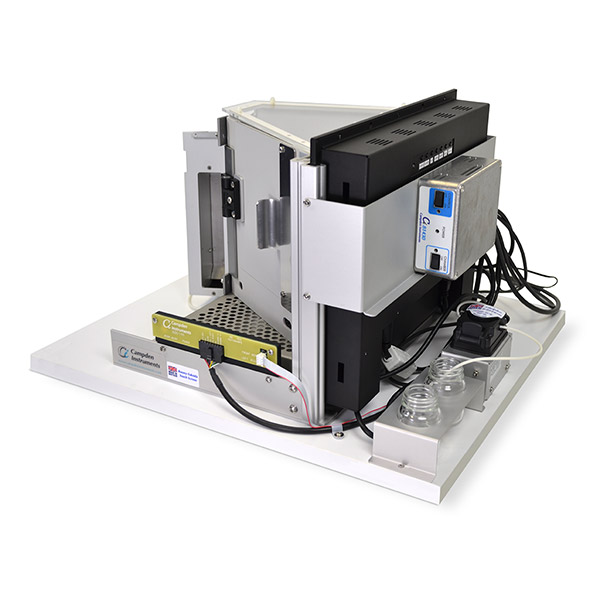


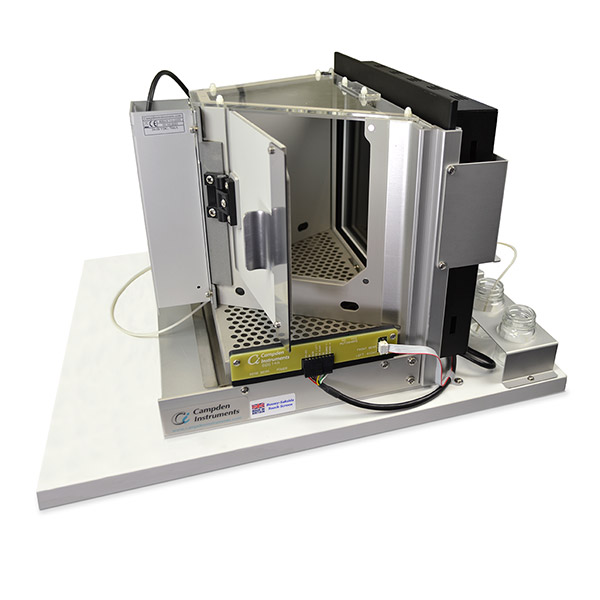
First developed in the 2009 at Cambridge University, the Bussey Saksida Rodent Touch Screen Chambers are now used by over 300 different Research Groups in at least 26 countries. The Bussey-Saksida Chamber has always featured a unique trapezoidal wall shape in order to focus the animal's attention and facilitates the efficient and high-throughput cognitive evaluation of rodents. The chamber is easily reconfigured to a modular square arena with panels, levers, lights, and a range of other operators to accommodate any task like an operant chamber equipped with a traditional lever or nose-poke.
The Second Generation Bussey-Saksida chamber was built with video in mind. New non-reflective walls and floors will aid video tracking, and IR and ambient lighting located under the chamber lid provide even lighting of the chamber and eliminate glare.
Many accommodations for tethers can be made including updated lid and open reward areas to accommodate headstages. A convenient sliding drawer can be added to the environmental cabinet to neatly store and feed the tether.
All electronic components are adjusted to reduce EMC. The environmental cabinet is a Faraday cage to prevent outside noise from the surrounding area from entering the chamber. Even the touch screen itself is shielded to reduce noise emission.
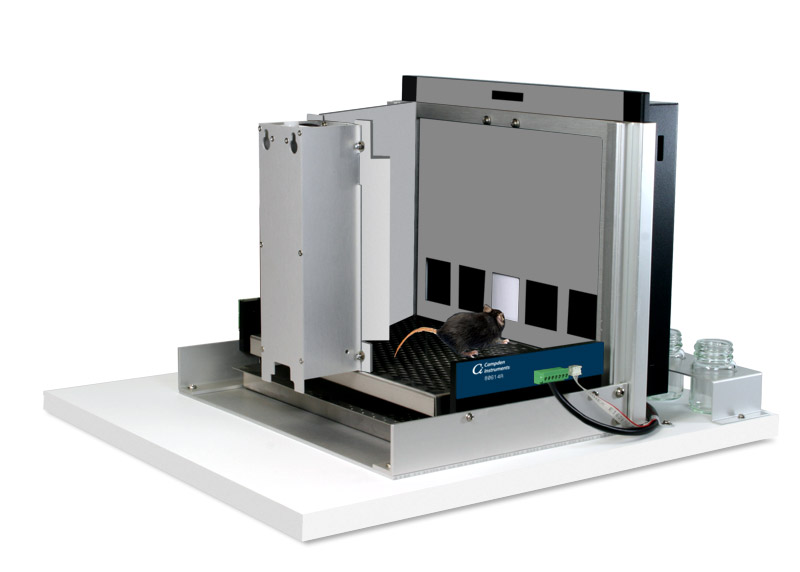

The Bussey-Saksida chamber allows usage of standard, original, and customized paradigms. Standard Task Paradigms are available by arrangement with the University of Cambridge. Standard tasks include popular Tasks such as PD, PAL, 5CSRT, PRC, Location Discrimination, and many more. The rodent tasks range from simple to complex and are virtually identical to tasks used with NHP & human populations on the CANTAB system. All paradigms include training routines as well as the main experimental paradigm and the data analysis sets.
| NHP/Human CANTAB Equivalent | Standard Tasks | Typical time to reach baseline | Example neural systems involved | Clinical area showing impairment |
| NHP | Pretraining to touch an image and initiate a trial (All task except Auto and 5CSRT) | 1-2 weeks (e.g., 7-8 week old C57BL6J mice: 5 days) | Learning | |
| Human/NHP | Pairwise / Visual Discrimination (PD) and Reversal Learning | Pretraining + 5-7 sessions test to reach base line | Prefrontal Cortex, Perirhinal Cortex, Anterior Cingulate, Posterior Cingulate, Medial Frontal Cortex, Striatum, Dopamine system, Cholinergic system, NMDA receptors. Mediodorsal Nucleus of the Thalamus | Huntington's, Schizophrenia, Parkinson's, Learning, Cognitive Flexibility, Executive Function. |
| Human/NHP | Paired-Associate Learning Task for Rodents (PAL) | Pretraining + 35-45 sessions to 70% | Hippocampus, Cholinergic system, NMDA Receptors, AMPA Receptors | Alzheimer's, Schizophrenia, Spacial Memory |
| NHP | Visuomotor Conditional Learning for Rodents (VMCL) | Pretraining + Approximately 20 sessions | Dorsal Striatum, Posterior Cingulate Cortex | Huntington's, Parkinson's |
| Human/NHP | 5-choice Serial Reaction Time Task for Rodents (5CSRT) | Pretraining (ave 10 sessions) + 3 weeks to 80% @ 2 sec baseline | Prefrontal Cortex, Basal Forebrain, Cholinergic (Accuracy), Serotonin (Impulsivity), Noradrenaline (Distraction), Dopamine (Motivation) | Alzheimer's, Depression, Huntington's, Schizophrenia, ADHD, OCD |
| Autoshaping for Rodents (Auto) | Several sessions (no pretraining required) | Ventral Striatum, Amygdala, Anterior Cingulate Cortex, Nucleus Accumbens Dopamine, Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus, D1 and NMDA receptors | Huntington's | |
| Human/NHP | Trial-unique Nonmatching-to-Location Task for Rodents (TUNL) | Pretraining + 6-24 Sessions to acquire the basic task | Hippocampus, Cholinergic system, NMDA Receptors, Prefrontal Cortex | Alzheimer's, Schizophrenia |
| NHP | Location Discrimination for Rodents (LD) | Pretraining + 10-20 sessions | Hippocampus, Neurogenesis | Alzheimer's, Schizophrenia |
| NHP | Extinction for Rodents (EXT) | Approximately 4 sessions training + a sessions days extinction | Infralimbic Cortex, Striatum and Amygdala | ADHD, OCD |
| Human | 5-Choice Continuous Performance Test for Rodents (5C-CPT) | Approximately 13 sessions (based on training in 5-hole box) after training to 5-CSRTT | Dopamine, Serotonin, Cholinergic, Parietal, Muscarinic. | Schizophrenia, ADHD, OCD, Alzheimer's |
| NHP | Progressive Ratio and Effort Related Choice Task for Rodents (PR/ERC) | 16 sessions from first habituation to reach stable PR performance | Dopamine | Motivation, Decision Making |
| Human | 4-Choice Gambling Task for Rodents (4C-GT) | Pretraining + 4 sessions familiarizing with choices available, then 13 sessions testing | Dopamine, Serotonin | Bipolar Disorder, Gambling, Depression, OCD, ADHD, Parkinson's, Schizophrenia, Impulsivity |
| Human/NHP | Rodent Continuous Performance Task: Image for Rodents (rCPT) | Pretraining + Approximately 30 sessions | Cholinergic system, Anterior Cingulate Cortex | Schizophrenia, ADHD, OCD, Alzheimer's |
| Human | Delay Discounting for Rodents (DD) | Pretraining + approximately 13 sessions | Dopamine | Impulsivity, ADHD |
| NHP | Probabilistic Reversal Learning for Rodents (PRL) | Pretraining + Approximately 17 sessions | Serotonin | Depression |
The Touch Screen has been used to develop a wide range of tasks, probing different areas of cognition, most of which are available ready written with programs and information to train the rodents to the task.
The design of the Touch Screen chamber and the tasks were both found to be crucial to get good and consistent results - comparable results have been achieved by labs all over the world using the Lafayette/Campden Touch Screen and these prewritten tasks. Implementation of the smooth trapeziodal walls and extra sensitive Touch Screens significantly reduced the training times and rodent performance – minimizing distraction and making sure all nosepokes to the screen are detected.
As well as being able to compare results with other rodent Touch Screen work, the chambers also lend themselves to comparing with both NHP and Human Touch Screen Tasks.
Human CANTAB was developed at Cambridge University, UK, from well-known animal models of behaviour. This has allowed the development of a range of cognitive tests proven to be sensitive to specific regions of the brain. These language free Human CANTAB tests have been further developed to make them suitable for monkey studies - incorporating as few changes as possible.
Monkey CANTAB was developed by a group including Drs T.W. Robbins and A.C. Roberts at the Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge, England, to improve the comparative assessment from animals to humans. The result is a battery of tests that can be used to study cognition in both experimental primates in the laboratory and humans in the clinic. Link to Monkey CANTAB Page
Professors Tim Bussey and Lisa Saksida at the Cognitive Systems Neuroscience Laboratory, University of Cambridge, England have also developed rodent touchscreen chambers and tasks for rats and mice to again find tasks that are translational to human cognitive tests.
An important consideration in the development translational tasks has been to maximise the likelihood that the same cognitive abilities are used by both animals and humans to perform each test. Consequently, complex tasks are broken down into their constituent elements and each element assessed independently of the next in a step-by-step progression through the test. Guiding a subject through the test in this way restricts the use of alternative strategies and permits an analysis of performance in terms of the cognitive components involved. Functional equivalence is suggested if the pattern of performance of animals and humans, at each stage of the test, is qualitatively similar and if comparable impairments are seen following damage to selective brain structures. A growing bibliography is building evidence that this is the case.
Key Paper - Touchscreen cognitive testing: Cross-species translation and co-clinical trials in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disease, Palmer et al, Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 2021, 107443.
One case in point concerns the Paired Associate Learning Task (PAL). In human studies early onset Alzheimer’s patients have shown significant deficiencies on this task. Humans with a DLG2 mutation have been found to be impaired on PAL. Likewise DLG2 knock out mice show impairment as shown here. [Nithianantharajah et al, Nature Neuroscience, 2013, 16]
Several strains of rats and mice have been used in the touchscreen chambers, including transgenic and knock out animals.
In a Lab Animal Review article it is also argued that the translational nature the tasks, the lack of aversive stimuli and the wide range of psychological constructs that can be evaluated, means the touchscreen method can yield significant 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction and Refinement) benefits.
Adapted for mice. As a measure of impulsivity, the Delay Discounting Task (DD) measures how long the rodent is prepared to wait for a larger reward.
Precision food dispenser with dispensing wheel that accommodates 14mg pellets.
Converts the 80614-07-01 to accept pellets. Can be configured to detect either a nose poke or pellet retrieval.
Adapted for mice, this is a simple, but powerful, test of behavioral inhibition.
Adapted for mice. Designed to measure sensitivity to valence feedback information, PRL is sensitive to serotonergic manipulations, suggesting this test may be used to study depression-relevant behavior.
Adapted for mice, this test is based on the Iowa Gambling Task, sensitive to serotonergic and dopaminergic agents.
Designed to fit the trapezoid walls of the Bussey-Saksida touch screen chamber, this alternative reward trough allows mice to take liquid reward without having to nosepoke into the reward trough.
Adapted for mice, this reversal learning task requires inhibition of prepotent responses and is known to be dependent on the prefrontal cortex.
Adapted for mice, this is a hippocampal task. In humans, this task has proved to be highly effective for the early detection of Alzheimer's disease.
Adapted for mice, this is a habit or stimulus-response task in which the rodent learns a conditional rule.
Adapted for mice, this task is sensitive to cortical manipulations, especially those involving prefrontal cortex, and is highly dependent on cholinergic transmission.
Adapted for mice, this touch screen task has been shown equivalent to those performed with levers or nose-poke holes in measuring motivation and reward-related decision making.
Adapted for mice. In this Rodent CPT (Image) task, 5 different images are shown briefly, one at a time and in a random order. One of the images is designated the target stimulus. In order to obtain reward, the subject must touch the target stimulus and withhold from touching the non-target stimuli.
Slotted chamber lid accommodating free tether movement with built-in under lid IR LED illumination and house light.
Reward trough for liquid feed/reward.
Adapted for mice, this is a working memory task. TUNL is a delayed nonmatching-to-place task that prevents the mediating strategies associated with the equivalent lever task.
Adapted for mice, this is a spatial memory task with a reversal learning component. It is sensitive to hippocampal lesions and associated with glutamate receptor regulation and signaling.
Adapted for mice, this task measures a Pavlovian response to the screen. This is a very rapidly administered test of simple classical conditioning that is dependent on a reward system centered on the ventral striatum.
Adapted for mice, this go/no-go task measures both attentional and inhibitory systems within a single task paradigm, enabling the assessment of vigilance.
Reward Trough for liquid feed using electronics with reduced electromagnetic emission and electrical isolation coating for better integration with electrophysiology recording.
The rate of flow for the Precision Liquid Feed Pump is been calibrated to give precise delivery of liquids at delivery rates suitable for rewarding mouse, rat, and primate.
The Second Generation Bussey Chambers with Intelli-interface supports up to 20 chambers on one PC. On the strength of 10 years of feedback and development, the system is even more flexible and with more features.
The Easy-install was developed for the Bussey-Saksida Touch Screen Systems due to the large number of cables and connections that these systems require.
ABET Core Intelli-interface is a smart interface which controls all aspects of your chambers including touchscreen and computer-generated audio.
From writing schedules to analyzing data, ABET Cognition gives you the powerful and flexible tools necessary to control a network of touch screen chamber systems.





















