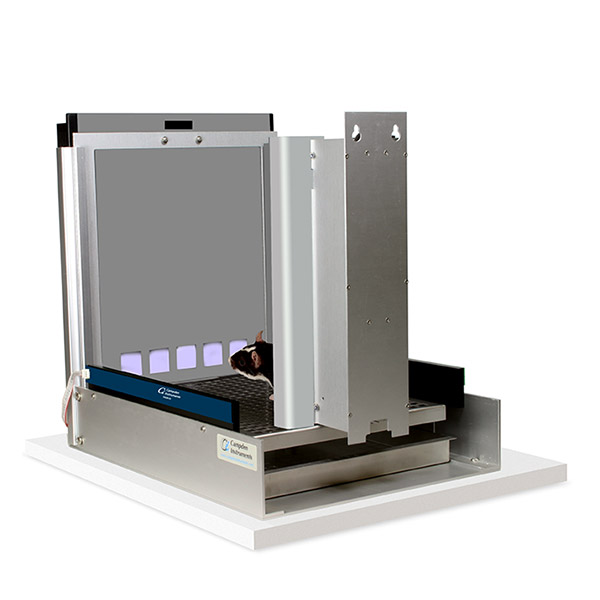
Like the 5-choice serial reaction task, this task requires the rodent to respond to a brief visual stimulus presented randomly in one of 5 locations. In addition. some trials present visual stimuli in all five locations together and for these trials the subject must learn to withhold a response. This go/no-go task measures both attentional and inhibitory systems within a single task paradigm, enabling the assessment of vigilance.
Cavanagh, J. F., Gregg, D., Light, G. A., Olguin, S. L., Sharp, R. F., Bismark, A. W., Bhakta, S. G., Swerdlow, N. R., Brigman, J. L., & Young, J. W. (2021). Electrophysiological biomarkers of behavioral dimensions from cross-species paradigms. Translational Psychiatry 2021 11:1, 11(1), 1-11. - Abstract
Braeckman, K., Descamps, B., Vanhove, C., & Caeyenberghs, K. (2019). Exploratory relationships between cognitive improvements and training induced plasticity in hippocampus and cingulum in a rat model of mild traumatic brain injury: a diffusion MRI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior. - Abstract
Arulsamy, A., Corrigan, F., & Collins-Praino, L. E. (2019). Age, but not severity of injury, mediates decline in executive function: Validation of the rodent touchscreen paradigm for preclinical models of traumatic brain injury. Behavioural Brain Research, 368. - Abstract
Braeckman, K., Descamps, B., Caeyenberghs, K., & Vanhove, C. (2018). Longitudinal DTI changes following cognitive training therapy in a mild traumatic brain injury rat model. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 12. - Abstract
The Second Generation Bussey Chambers with Intelli-interface supports up to 20 chambers on one PC. On the strength of 10 years of feedback and development, the system is even more flexible and with more features.
