17 March
2025
17 March
2025

Campden Instruments Announces Distribution Partnership with SDR Scientific for Australia and New Zealand
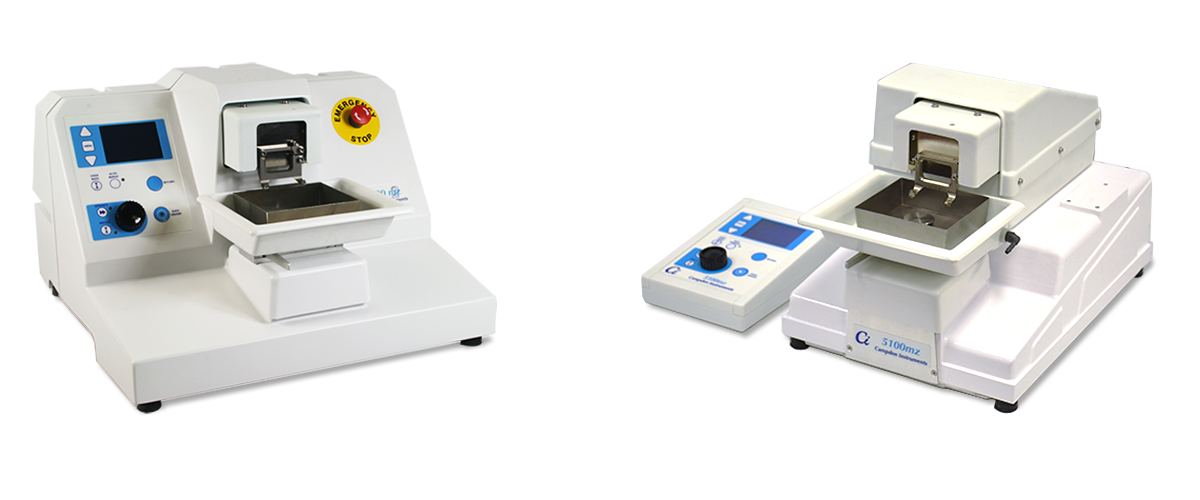
Campden Instruments, a leading manufacturer of vibrating microtomes, is pleased to announce a new partnership with SDR Scientific, a renowned life science distributor covering both Australia and New Zealand. This collaboration marks a significant step in expanding Campden’s presence and delivering enhanced service to their customers.
Through this partnership, SDR Scientific, based in Sydney, Australia will serve as an official distributor of Campden Instrument’s vibrating microtomes, making them more accessible to researchers in Australia and New Zealand. Customers will benefit from improved product availability with faster delivery times, and superior local technical support.
“SDR Scientific shares our commitment to high-quality products, and customer satisfaction,” said Dr Ian Davies, Managing Director of Campden. “This partnership enables us to better serve researchers in Australia and New Zealand, by providing them a reliable contact for great service in their time zone and continent.”
SDR Scientific brings extensive experience in the life science sector making them an ideal partner for Campden. “We are excited to begin distributing Campden Vibratomes,” said Simon Rushworth, Managing Director of SDR Scientific. “Their high-quality vibratomes align perfectly with our commitment to providing superior solutions for our customers. Together, we look forward to creating new opportunities for researchers here in Australia and New Zealand.”
About Campden Instruments
Campden Instruments, a part of Lafayette Instrument Group is known for turn-key solutions for translational life science research. With a commitment to excellence and customer satisfaction, Campden Instruments continues to drive innovation in vibrating microtomes and deliver industry-leading solutions for animal behaviour for scientists across the globe.
About SDR Scientific
SDR Scientific is a leading distributor of quality scientific and clinical hardware, software and consumables to scientific research, medical and industrial customers in Australia and New Zealand. Known for its strong customer relationships and extensive distribution network, SDR Scientific is dedicated to providing the highest-quality equipment and service available.
A copy of the Press Release can be downloaded here
20 May
2024
20 May
2024
For Immediate Release
LAFAYETTE, IN - May 7th, 2024 - Lafayette Instrument receives CE MDR (Medical Device Regulation) approval for Evaluation products.
Lafayette Instrument, an Indiana based manufacturer of specialized scientific instruments is compliant to the EU Medical Device Regulation requirement for CE marking two medical devices for sale into the European Union.
The 01165A series Hand-Held Dynamometer is a valid and proven assessment tool used for objectively quantifying muscle strength.
The Pneumograph is a non-metallic bellows assembly designed for respiratory and cardiac gating in MRI applications.
Brent Smitley, Quality and Compliance Manager noted "Lafayette Instrument Company is now registered on the EU database and our products are now listed under LIC at the EUDAMED site."
We are excited to have restarted shipping the Hand-Held Dynamometer into Europe with CE MDR compliance.
21 April
2023
21 April
2023

Lafayette Muscles up! Acquires Aurora Scientific
Bringing together two leaders of Instrumentation for Life Science
Lafayette, Indiana U.S.A. (April 21, 2023)
Lafayette Instrument Co. is pleased to announce its acquisition of Aurora Scientific Inc. on April 17, 2023. Both Lafayette Instrument and Aurora Scientific have decades of experience serving the life sciences research community and expect a seamless integration.
"This partnership brings together two leading instrumentation companies within life science community, and presents an opportunity to strengthen our relationships with top research institutions and broaden our product offering." said Benjamin Mangrich, CEO of Lafayette Instrument.
As a result of this acquisition, Lafayette Instrument expands its scientific instrumentation line of products serving world-leading academic institutions the most innovative and high-performance solutions and service available in the industry.
Geoff Chandler, President of Aurora Scientific will be staying on with the organization said, "We are excited to partner with Lafayette Instrument to grow our business and expand our customer base."
1 June
2022
1 June
2022
The authors present a self-paced protocol, suggesting quicker results may be obtained using mouse models.
Abstract
The five-choice serial reaction time-task (5-CSRTT) is a behavioral rodent test that can assess executive
functioning. It may be employed to analyze distinctive aspects of murine models for a plethora of diseases, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, Alzheimer’s Disease, autism, and schizophrenia. The test has been performed primarily in rats and, although more challenging to apply to murine models, has the benefits of more diverse genetic models. The task is mainly based on training animals to nose-poke a lit screen within a stimulus duration time. Animals that perform a trial within the stimulus duration (SD) time receive a food/liquid reward. From training to experimental steps, classical 5-CSRTT can take more than 40 days to perform; however, here we present a murine self-paced, liquid reward-based 5-CSRTT (SP5C), using the ABET II system. Our version of SP5C can render competent results in ~14 days. We believe that, with this self-paced protocol, quicker results may be obtained using mouse models. Hence, a greater diversity of genetic models and diseases can be explored to expand our knowledge of complex polymorphic diseases, providing an additional platform for preclinical pharmaceutical testing.
Reference
Cunningham, J., Sheppard, L. D., Listik, E. and Wang, Q. (2022). Self-Paced Five-Choice Serial Reaction Time-Task for Mouse Behavioral Testing. Bio-101: e4388. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4388.
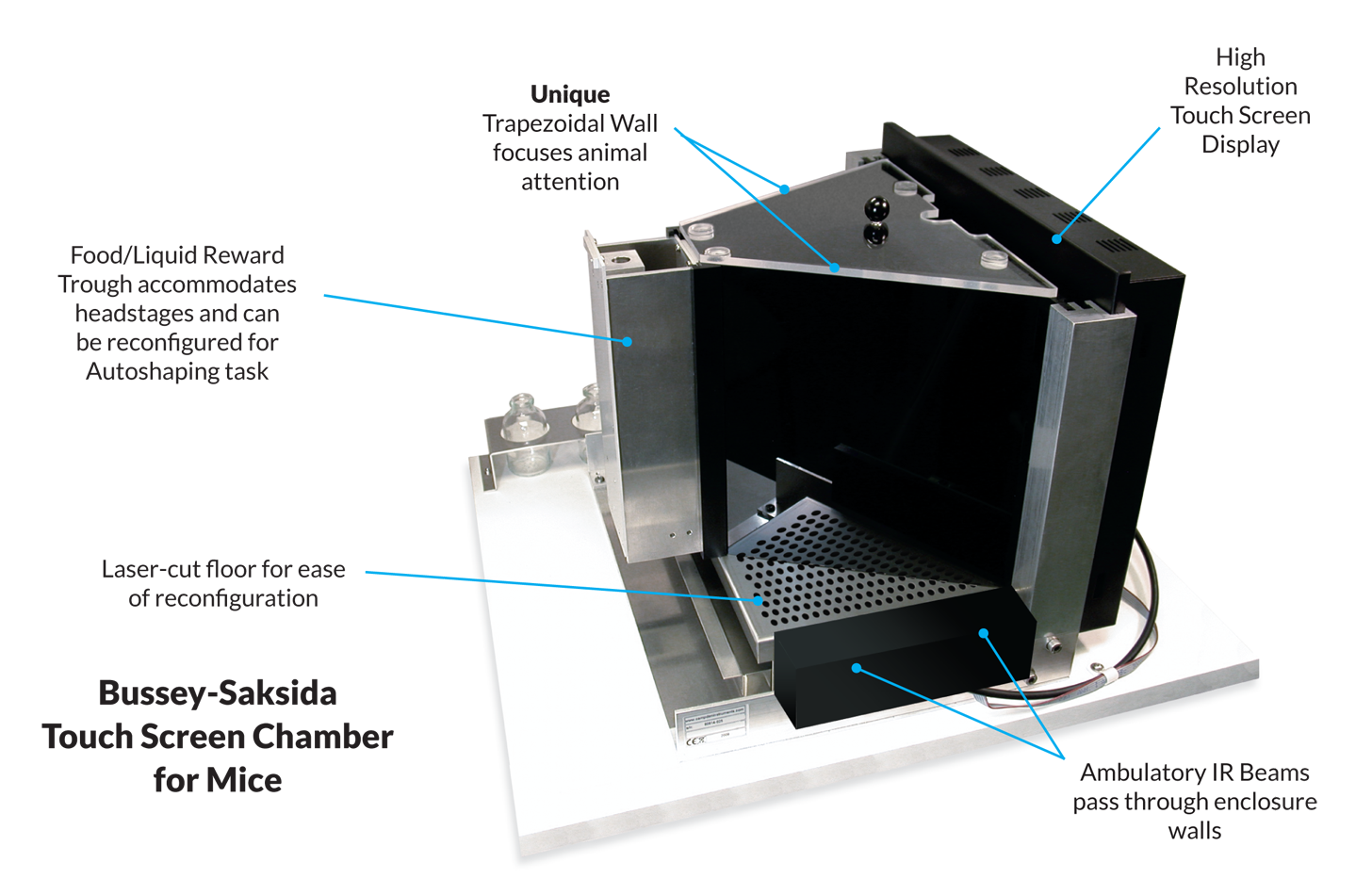
Our complete line of Rodent Touch Screen Chambers can be viewed here.
5 October
2021
5 October
2021
A new article written by groups from University of Cambridge (UK), Western University (Ontario, Canada) and the Open University (UK) has reviewed the value of touchscreen use in addressing the principles of the 3Rs.
Abstract
Despite considerable advances in both in silico and in vitro approaches, in vivo studies that involve animal model systems remain necessary in many research disciplines. Neuroscience is one such area, with studies often requiring access to a complete nervous system capable of dynamically selecting between and then executing a full range of cognitive and behavioral outputs in response to a given stimulus or other manipulation. The involvement of animals in research studies is an issue of active public debate and concern and is therefore carefully regulated. Such regulations are based on the principles of the 3Rs of Replacement, Reduction and Refinement. In the sub-specialty of behavioral neuroscience, Full/Absolute Replacement remains a major challenge, as the complete ex vivo recapitulation of a system as complex and dynamic as the nervous system has yet to be achieved. However, a number of very positive developments have occurred in this area with respect to Relative Replacement and to both Refinement and Reduction. In this review, we discuss the Refinement- and Reduction-related benefits yielded by the introduction of touchscreen-based behavioral assessment apparatus. We also discuss how data generated by a specific panel of behavioral tasks developed for this platform might substantially enhance monitoring of laboratory animal welfare and provide robust, quantitative comparisons of husbandry techniques to define and ensure maintenance of best practice.
Reference
Lopez-Cruz, L., Bussey, T.J., Saksida, L.M., Heath, C.J. (2021) Using touchscreen-delivered cognitive assessments to address the principles of the 3Rs in behavioral sciences, Lab Animal, 50, 174-184.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41684-021-00791-2
Our complete line of Rodent Touch Screen Chambers can be viewed here.