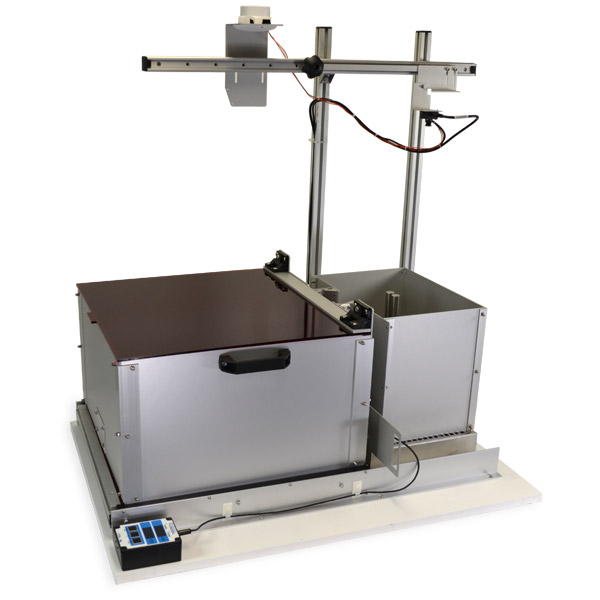

Novel Object Recognition and Object Location Recognition have long been used with rats and mice as a test of memory. It relies on the rodent's natural behaviour and does not require any food restriction.
Whereas the prevailing one trial a day methodology has inherent limitations and is subject to variability across labs, mainly due to the amount of animal handling that is required, Easton's "Continuous Trials" NOR method enables up to 16 trials a day without handling between trials and was developed with supported from an NC3R's project in four UK universities.
The advantages of "Continual Trials" are as follows:
Manual Scoring App is available for easy manual capture of the data.
IIn "Continual Trials" methodology, the animal moves between home-cage and experimental chamber under its own natural motivation, allowing multiple trials per session. Typically 16 trials can be performed within a 2 hour session.
Diagram of the stages of our modular system (PDF)
With the fully automated chamber the gate opening, monitoring when the animal crosses through the gate in either direction, dispensing of food to encourage shuttling between the holding and experimental chamber and the turning on of the monitoring cameras are all computer controlled. The experimental technician need only worry about changing the objects, and our handy control console will tell you when this needs to be done and which objects to place in the chamber. The cNOR-OL Auto-Chamber Operators Console for ABET II (Model CI.80514-1) also allows communication to the control system that the objects have been changed.
In addition to the fully automated chambers, our budget chambers with just a manual gate can be purchased and these can be upgraded to the automated chamber. Adding our cNOR-OL Operators Console for Manual Gate and Chamber (Model CI.80514-2) aids temporal control of the four stages of each trial.
The NC3Rs recognizes the Continual Trials apparatus meets goals of number of animal use reduction and refinement by reducing the necessary handling. For more information about the goals of the NC3Rs and the 3Rs, visit the NC3Rs website.
There is also an option to have changeable floors in the cNOR-OL chamber. This adds an extra context, so the mice have to remember the object, the place they last saw it and on what context floor it was on. This is a measure of episodic memory. The Easton Lab have further investigated rat strategy in doing the test - Read More
Rat cNOR-OL manual gate with microswitch for camera trigger.
Rat cNOR-OL Auto-gate with 'E' and 'H' chamber photobeams, recording direction of travel and camera trigger.
A fixed grid floor option for the Rat cNOR-OL Experiment and Holding Chamber. A changeable sliding floor is also an option to add a further context.
A combined reward trough and pellet delivery to fit Rat cNOR-OL Experiment and Holding Chamber.
Rat cNOR-OL Experiment chamber sliding floor with magnetic mounting for changing context floors for measures of Episodic Memory.
Five context change floors of different textures for Rat cNOR-OL Experiment chamber. Enables the chamber to be used for the” Object-Place-Context (OPC)2 Task (also known as the "What-Where-Which" Task) for Episodic Memory.
Rat cNOR-OL camera mount sub-assembly with speaker for white noise.






